User Logon, Global Catalog, and Domain Controller
In Active Directory, a domain controller (DC) performs authentication and issues authorization data (for example, group memberships).
A Global Catalog (GC) is a directory service that helps the forest locate objects and evaluate certain logon requirements quickly.
This page summarizes the cases where a Global Catalog server is commonly involved.
When a Global Catalog server is required
The following scenarios commonly require a GC in a multi-domain forest:
-
Forest-wide searches
A Global Catalog server provides fast searches across all domains by answering queries against the GC dataset. GC searches commonly use LDAP port 3268 (or 3269 for TLS). -
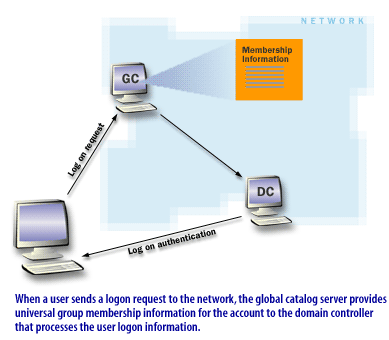
User logon with universal group membership
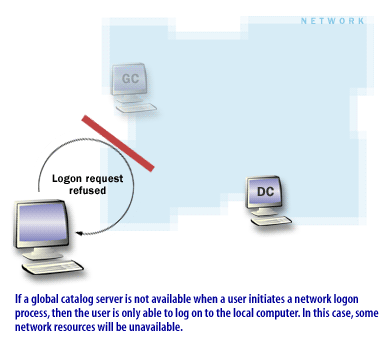
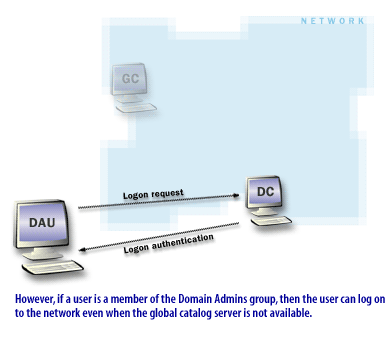
When a user belongs to universal groups, the authenticating DC may need GC information to evaluate those memberships during logon and authorization. If a GC is unavailable across sites, logon can be delayed or fail depending on site design and caching. -
UPN logon in a multi-domain forest
When users log on with a User Principal Name (UPN) (for example,[email protected]) and the forest contains multiple domains, the GC is used to resolve the name to the correct account location. -
Universal Group Membership Caching (UGMC)
In sites that have domain users but no local GC, UGMC can cache universal group membership information after the first successful logon. This reduces repeated WAN lookups to a remote GC and can improve logon reliability for branch locations.
Operational takeaway: in most enterprise designs, you either place a GC in the site or you enable UGMC to avoid hard WAN dependency for logons that need universal group data.
Security note: avoid obsolete tooling and cryptography (for example, RSH and DES). Favor modern remote administration (PowerShell Remoting/WinRM or SSH) and modern cryptographic suites (AES with SHA-256+).